Initially, the tendon is very weak and you may experience swelling as your body sends chemicals to heal the tendon and the tissues that have been damaged.
2 min read 21 Jul 2023
Understanding Tendon Repair
Initial Phase
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Weeks 1-3
Weeks 4-7
Weeks 8-12
Workplace Communication
It’s vital to maintain open dialogue with your employer to ensure they’re aware of the extent and nature of your injury. If possible, it’s advisable to resume work duties that only require one hand.
Exercise and Maintenance
For the best outcomes, strictly follow the exercise routine designed by your hand therapist. While the hand is recovering, keep all your other joints active to maintain their health. Your therapist will provide guidance on which joints to mobilise and which ones to keep static.
Other Considerations
Before you get back behind the wheel, consult your car insurance provider. Typically, a waiting period of twelve weeks is required post-surgery.
For further details and treatment options, please reach out to us.
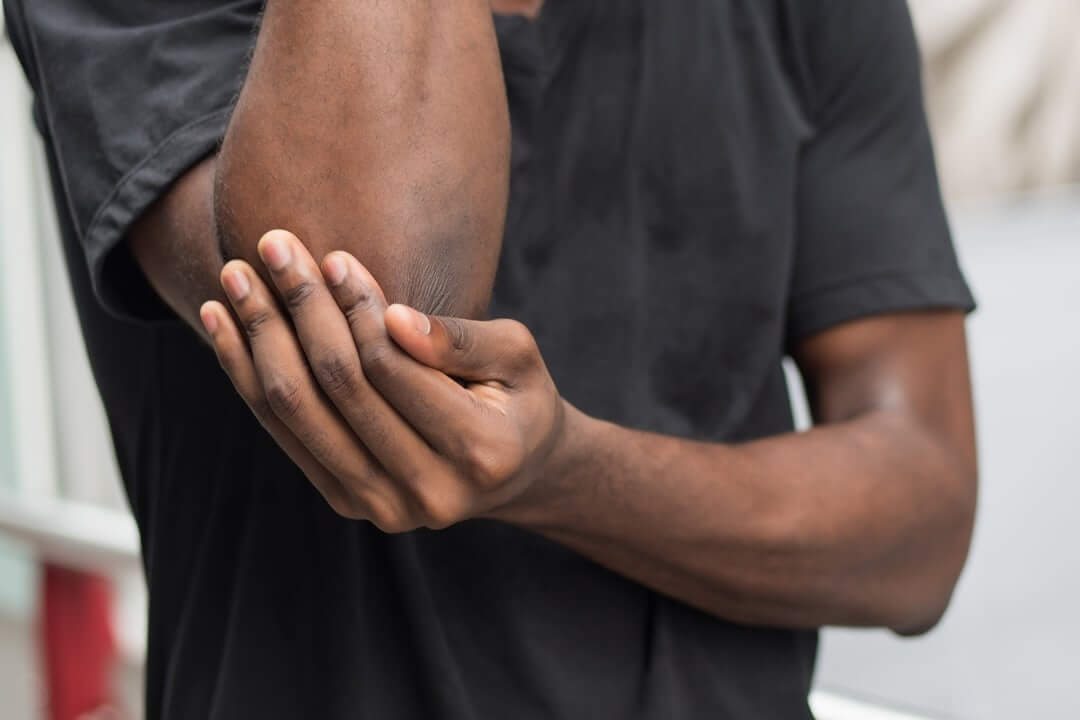

Acute pain is when the body is working to heal structural tissue damage. Everything is done to ensure structural and mechanical integrity if maximised of the injured tissues.

Most wounds recover in the repair phase of healing. Our therapists look after your wounds by providing dressings that are applied with a sterile technique to avoid infection.
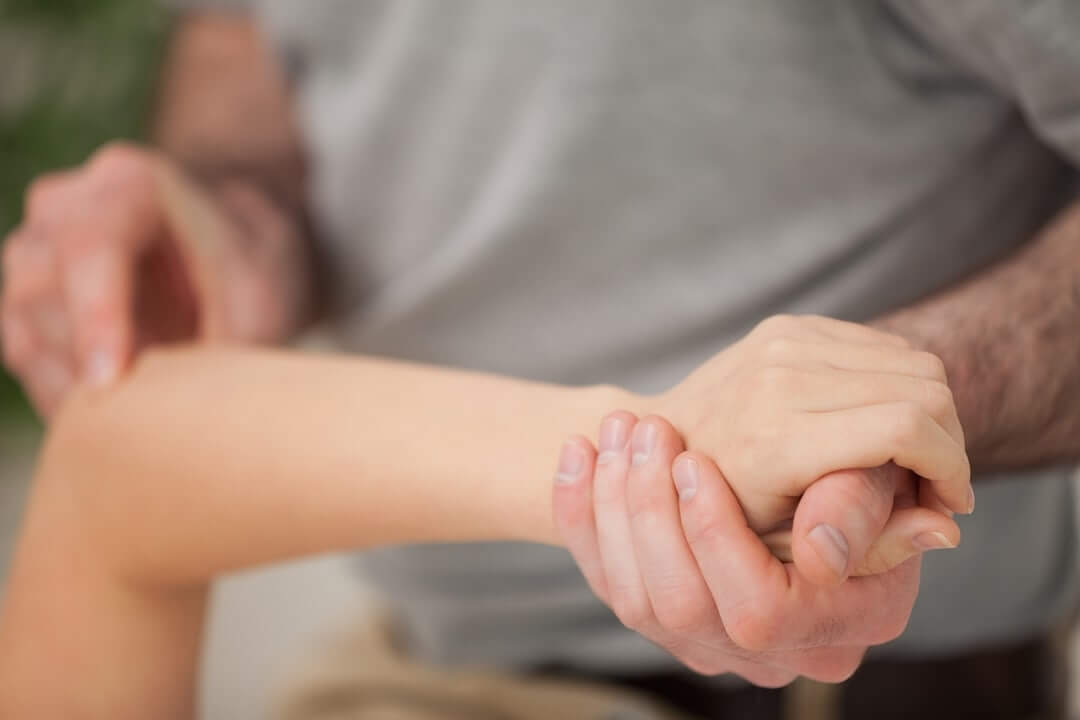

Joint mobilisation involves moving the joint back and forth in small oscillating movements further and further into range to restore the joints normal movement.
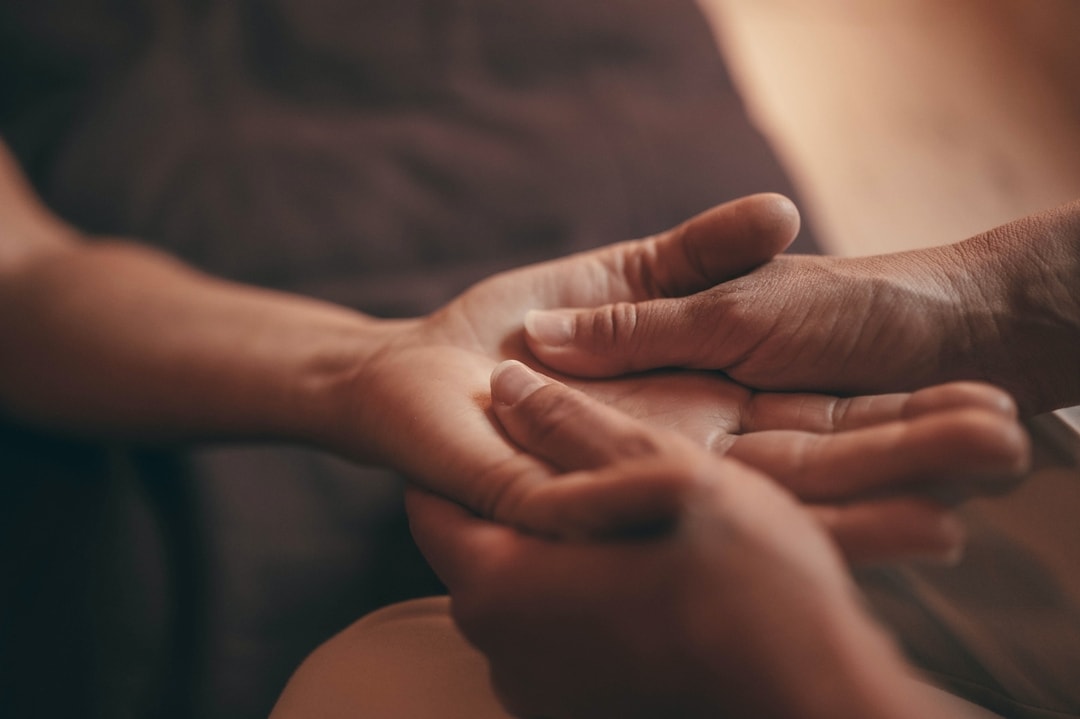

Massage helps to improve blood supply to the injured area, helping you recover faster.
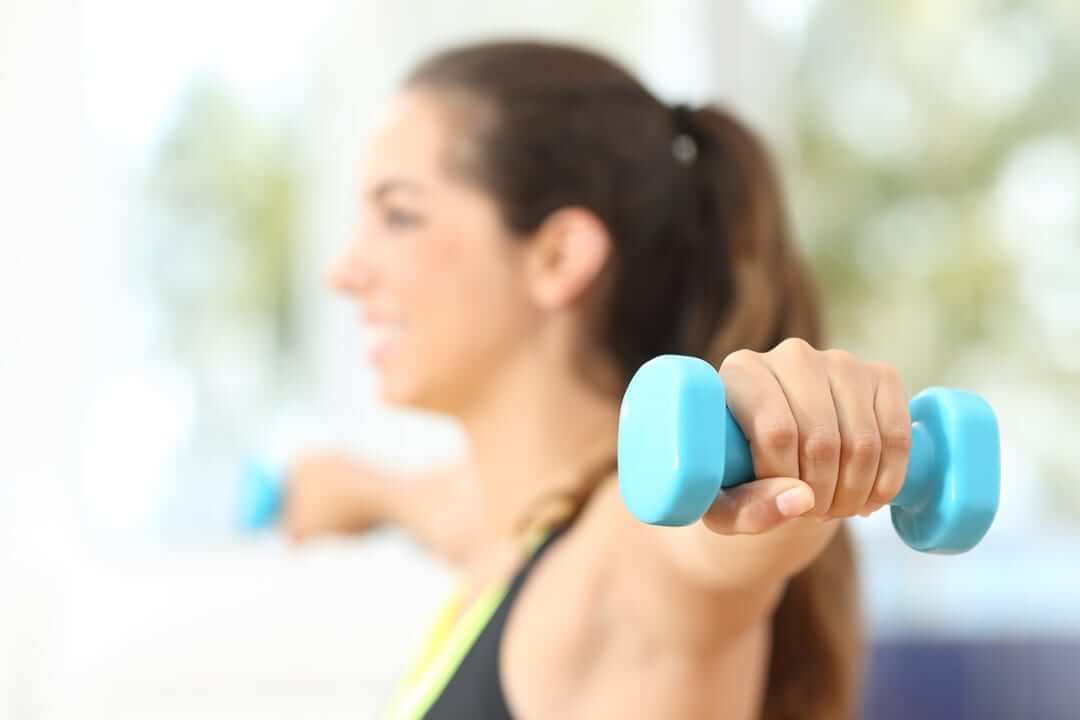

Exercise is the body’s natural way of restoration to improve stability, mechanics, strength and movement to an injury. Whether the injury is from overuse, trauma, disease or surgery exercises are necessary to restore function.
Stretching is extremely beneficial for our joints, muscles and tendons. Not only do they help prepare your body work/exercises they ensure you are working at your optimum energy efficiency.